In the modern world, prostatitis occurs in nearly 50% of the male population. The disease not only causes pain and discomfort, but can also have very unpleasant consequences, up to infertility. Therefore, every man should know how prostatitis manifests itself. Men's health and reproductive capacity largely depend on it.

Knowing the signs of prostatitis and periodic examinations by a doctor guarantee timely recognition and successful treatment of the disease.
Etiology of the disease
Prostatitis is a urological disease of inflammatory etiology. The disease can be caused by many factors.
The classification of prostatitis depends on what caused the prostate disease, how common the process is, and what the nature of the change is.
The following classification criteria are distinguished:
- The appearance factor is stagnant and contagious. In the first case, the problem is not due to an infection, but because venous blood or secretions are stuck in the pelvic organs. The second involves the entry of pathogenic microorganisms into the prostate gland. There is also prostatitis of mixed origin.
- Damage area. In case of prostatitis, the gland can become inflamed in different ways. This can be a chronic or acute form of the disease, which in turn is divided into parenchymal, chronic and follicular inflammation. The lesion may be sclerotic in nature or manifest as an abscess. This category also includes atypical chronic prostatitis, the symptoms of which do not correspond to the classic picture of the disease.
The symptoms of the disease also depend on the underlying cause. The infectious form occurs due to the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the prostate through the genitals, or it develops against the background of a chronic infection.
Non-infectious prostatitis can be triggered by a weakened immune system, hypothermia, sedentary lifestyle, abstinence from sexual intercourse, or, on the contrary, excessive sexual activity. Each case requires a different treatment.

Prolonged lack of sexual intercourse causes stagnation of prostate secretion and the development of congestive prostatitis.
Depending on which form you are diagnosed with, the signs and symptoms of prostatitis may vary. Self-treatment is strictly prohibited, as an ignorant person may mistake the manifestation of one disease for another, for example, inflammation of the prostate with spermatitis, vesiculitis, urethritis or benign hyperplasia. Improper treatment can have extremely sad consequences.
General symptoms
How is prostatitis manifested? If you do not take into account a specific type, the disease can manifest itself with the following typical symptoms:
- severe pain, which is first localized in the urinary tract, and then spreads to the entire groin and abdominal region;
- pain is constantly present in the scrotum and perineum, especially during urination and erection;
- during erection, the genital organ cannot reach the size it previously reached;
- the sexual relationship is shortened.

Symptoms can appear together or separately. If we talk about pain, then its intensity largely depends on the form and extent of the disease. Unfortunately, at the initial stage, many patients do not pay attention to such manifestations, due to which the disease progresses and can turn into chronic prostatitis, which is dangerous for the appearance of infertility.
If a man began to observe such symptoms in himself, then the risk of prostatitis is high and he should immediately seek professional help.

Even minor manifestations of prostatitis warrant a visit to the doctor.
Symptoms of acute bacterial prostatitis
Bacterial prostatitis is a form of the disease caused by an infection. It easily turns into chronic prostatitis, so you need to seek help immediately.
Acute bacterial prostatitis is often a secondary manifestation that accompanies any disease of the pelvic organs and has similar symptoms.
Acute bacterial prostatitis can be associated with the following symptoms:
- rise in body temperature;
- a feeling of chills accompanied by trembling of the muscles;
- pain in the prostate area;
- pollakiuria and stranguria;
- the spread of pain in the lumbar region and throughout the perineum;
- urination problems.

If the patient passes the tests, the disease can be suspected in the following cases:
- an increase in the number of leukocytes in the blood;
- bacterial cells are present in the secretion of the prostate;
- cloudy, whitish urine with a pH above 7. 0.

Characteristic changes will be present during the analysis of urine associated with prostatitis.
These are the main signs of acute bacterial prostatitis. If you do not pay attention to them and do not start treatment, then the acute form will soon turn into chronic, the signs of which every man should also know.
Symptoms of chronic bacterial prostatitis
Chronic prostatitis develops as a result of neglecting the treatment of the acute form of the disease and is characterized by periods of exacerbation and remission.
For a man, it can be a discovery that he once had acute prostatitis, was allegedly treated and recovered, but after a while the symptoms of the disease (albeit in a milder version) reappeared. In such cases, it is worth thinking about the chronic course of the disease.
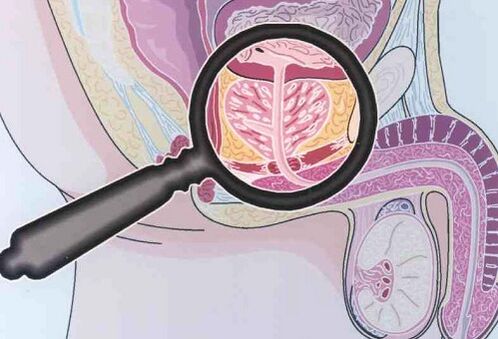
The lack of pronounced symptoms is dangerous due to the late accidental recognition of chronic prostatitis, already in an advanced form.
Chronic prostatitis does not have clear manifestations, which often leads to serious complications.
However, in such a situation, it is worth paying attention to:
- burning and cutting (sometimes bordering on unbearable pain) during a trip to the toilet and sexual excitement;
- constant desire to urinate, at least once every hour, at the end of the process the feeling of complete emptying does not occur;
- there is a burning sensation in the urethra during and after going to the toilet;
- the pressure in the jet is weaker than before - the flow may even be interrupted;
- constantly wants to go to the toilet at night;
- an unpleasant burning sensation remains in the genitals after sexual intercourse;
- ejaculation happens quite quickly;
- insomnia and causeless anxiety are observed.
These main symptoms of chronic prostatitis can easily be confused with sexual disorders. The problem is that few men can admit this to themselves. Therefore, they begin to self-medicate, the purpose of which is to restore sexual power, which only leads to the complication of the situation.
The insidious nature of chronic bacterial prostatitis is that it requires continuous monitoring, otherwise infertility may develop, the diagnosis of which can only be established after a comprehensive diagnosis of the patient.
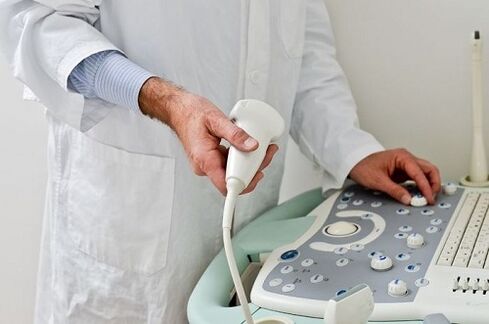
A complete examination to detect prostatitis necessarily includes an ultrasound examination.
The symptoms of the disease can manifest in different ways, and this applies not only to chronic but also to acute bacterial prostatitis.
It depends on the number of bacteria in the body and the body of each patient. As soon as the pathogenic organisms start to activate and multiply, the person starts to get worse. If the patient also leads an unhealthy lifestyle (smoking, exercising little, consuming alcohol and harmful products), then it should not be surprising that the disease continues to progress.
Non-bacterial prostatitis and its manifestations
Abacterial prostatitis is also quite common. It would be useful to know what symptoms may occur in this case. The pathology is characterized by the regular occurrence of pain, and not only during intercourse or going to the toilet.

Abacterial prostatitis is characterized by a frequent nocturnal urge to go to the toilet and an excess of nighttime urine compared to the daytime amount.
In addition, the following manifestations are associated with non-infectious prostatitis:
- pain in the genitals;
- pain and discomfort in the groin area;
- nocturia and testicular pain;
- decrease in the amount of urine excreted;
- difficulty starting the urination process;
- pain from the lumbar and perineal regions gradually moves to the lumbar region;
- pain in groin, coccyx, and pubic bone;
- discomfort after defecation.

Psychological discomfort is associated with physical suffering during the disease.
Signs of the disease may be accompanied by psychological disorders. The patient becomes irritable, as he is constantly tormented by pain and discomfort.
If measures are not taken in time, then a man may fall into depression, and he should seek help not only from a urologist, but also from a psychologist.
It should be noted that the clinical picture of atypical prostatitis can be similar to many other diseases, and asymptomatic prostate disease has no pronounced manifestations at all. Therefore, it is very important to consult a qualified doctor, who prescribes a number of diagnostic measures and tests - urine, blood, semen analysis, ultrasound, if necessary, biopsy, etc. Only then will the doctor make the correct diagnosis. and prescribes appropriate treatment.
Most often, a biopsy is performed to rule out a malignant process.
Knowing the symptoms of prostatitis is important for every representative of the strong half of humanity to find out what disease is bothering him, since the functioning of the entire urogenital system depends on it. And the sooner a man asks for help, the sooner he will be relieved.